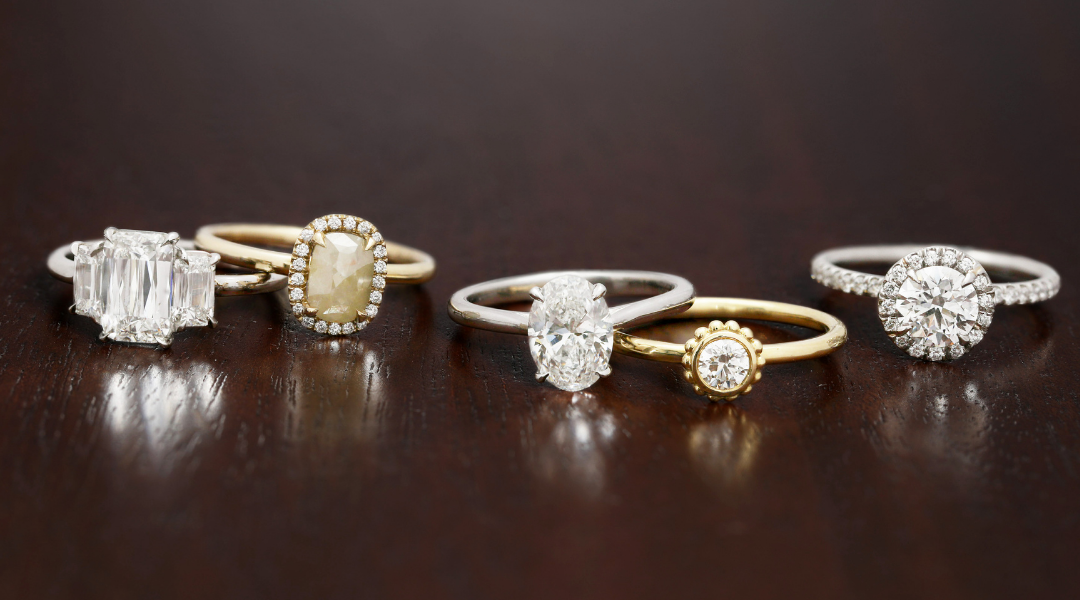
The TIVOL Diamond Guide
Are you feeling overwhelmed as you start looking at diamonds? We’ve simplified everything you need to know when shopping for the right diamond. You’ve already done the hard part. You found the one you want to spend the rest of your life with. Now let us help you find the perfect diamond to seal the deal.

The 4 C's:
- Cut
- Color
- Clarity
- Carat
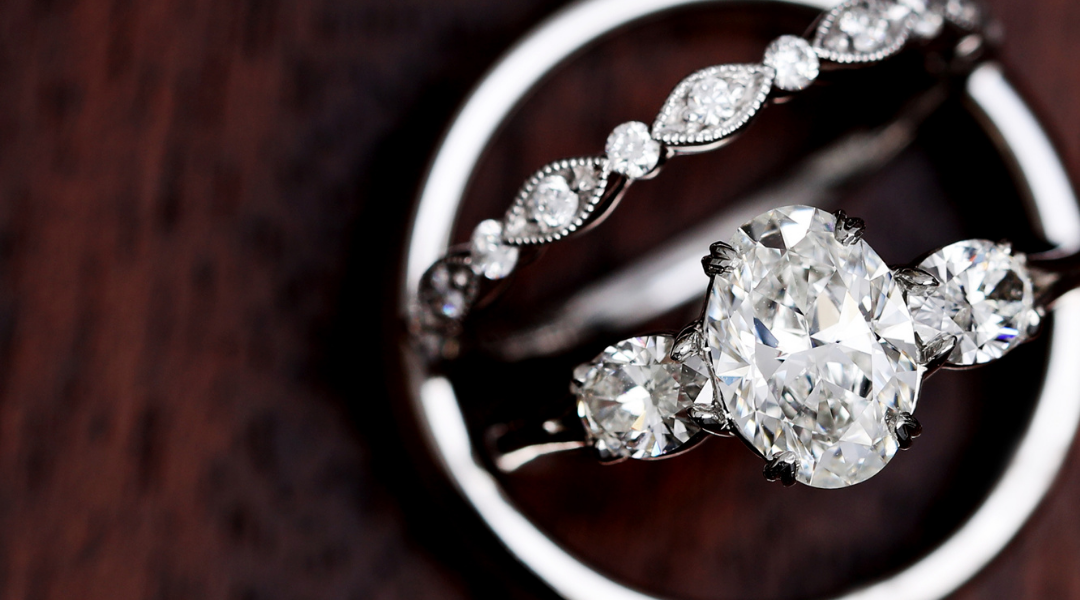

CUT: Cut refers to the proportion/precise placement of angles of the diamond’s facets. Diamonds that are cut too deeply or too shallow will lose light through the sides or bottom, making the diamond appear less brilliant.
Excellent cut diamonds absorb and reflect light efficiently, giving the diamond the greatest possible brilliance and flashes of light, known as “fire.”
Diamonds that are too shallow allow light to escape through the bottom rather than reflecting it out through the top. Diamonds that are too deep lose light by reflecting it out through their sides, reducing their overall brilliance.
While the cut refers to the quality and level of brilliance, shape is an aspect of the cut. Choose the shape you like best—some more non-traditional cuts go in and out of fashion, but ultimately it’s important to select the shape that matches your personality.
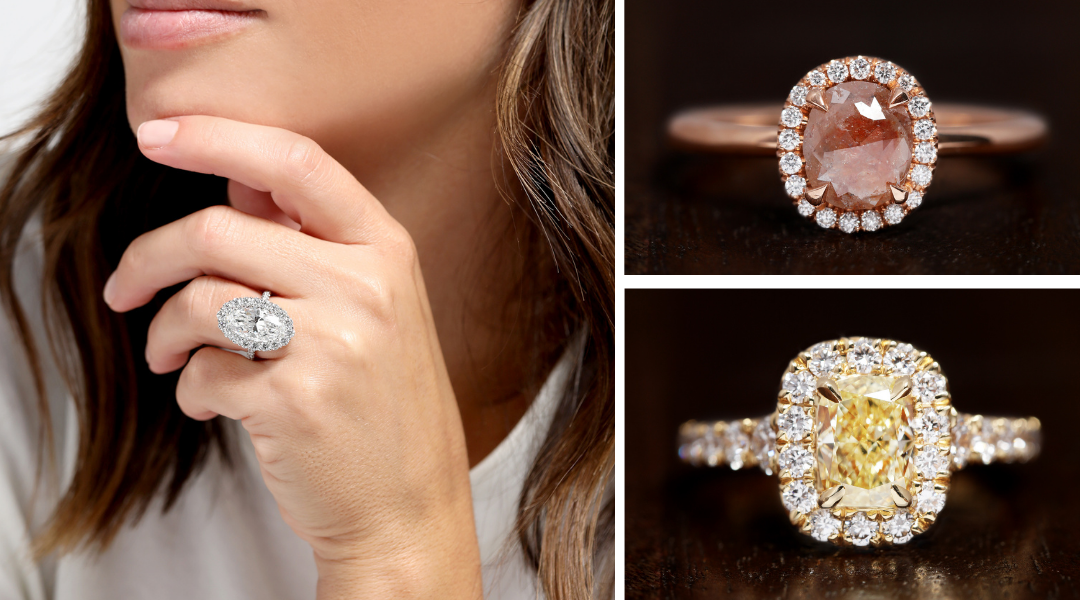

COLOR: Although many diamonds appear colorless, most still have varying degrees of yellow, brown or gray. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) has created a color grading system that is an industry standard. While a wide range of color grades are acceptable, the most sought-after grades are either colorless or near colorless.

CLARITY: Clarity refers to characteristics of the diamond called blemishes or inclusions. Inclusions are enclosed within a diamond, or they extend into the diamond from its surface. Blemishes are confined to the diamond’s surface. Inclusions typically have more influence on a diamond’s clarity grade than blemishes. Gemologists study the size, location, type and number of such characteristics to determine a clarity grade. Flawless and near flawless diamonds are very rare, and diamonds containing more or larger inclusions are more common. It should be noted that clarity characteristics make every diamond unique. It’s extremely unlikely that two diamonds would have the exact same clarity characteristics. This quality helps identify individual diamonds, giving each one its own unique fingerprint.

CARAT: Carat is the unit of measurement for the weight of a diamond. Commonly sold carat weights range from 0.25ct to 5ct, but there are variations beyond this—both smaller and larger.